heat loss from Passivhaus. Source:
Defining green building is not easy; for many, all that matters is energy consumption. One of the major ways of reducing consumption is to increase the amount of insulation, but that is only one component, and not necessarily the most important one.
Earlier this week
and we might as well enjoy it before they put their pay wall in the new year. Tim McKeough does a good interview with industrial designer Yves Béhar, who is optimistic about the future of green design:
What about sustainability?
Sustainability calls for a complete overhaul of every sector of production. That means that in the next 10 to 20 years, every process, every factory, every logistics system, every product, every service is going to have to be completely rethought from a sustainability standpoint.... Read the full story on TreeHugger
Ford Bringing Hybrid Tech to Conventional Cars
by: Eco Geek Latest, 2010-12-29 16:34:33 UTC

Some of the technology that helps make hybrid vehicles so efficient will soon be making its way into non-hybrid cars as well. Ford has recently announced that Auto Start-Stop technology, which has been used in gasoline-electric hybrids since 2004, will be introduced in some conventional cars, crossovers and SUVs in North America starting in 2012. Auto Start-Stop automatically turns off the engine when the vehicle comes to a stop, and then restarts it again when the vehicle is ready to move again.
Using Auto Start-Stop will increase fuel economy in city driving by at least 4 percent up to as much as 10 percent, depending on the particular vehicle size and usage. Auto Start-Stop also reduces all tailpipe emissions to zero when the vehicle is at a stop.
Ford is already making Auto Start-Stop available in Europe. According to Ford, "is standard on the ECOnetic models of the Ford Ka and Mondeo, and is launching now on Focus, C-MAX and Grand C-MAX." In North America, Auto Start-Stop will be available on hybrid models of the Escape and Fusion, as well as Lincoln MKZ.

The Roof That Goes Up in Smoke by Overtreders W
by: Dezeen, 2010-12-27 11:47:56 UTC
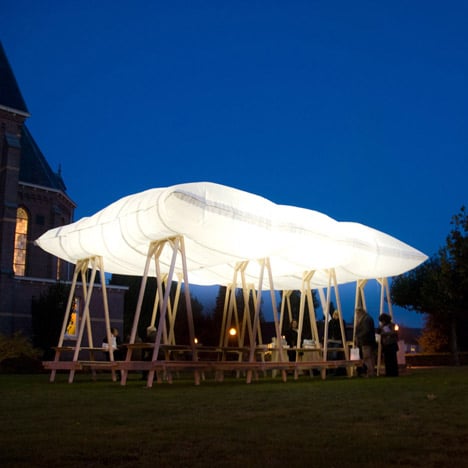

This inflatable pillow on stilts is a picnic pavilion designed by Netherlands design studio Overtreders W. (more…)



Fireclay Turns Toilets Into Tiles
by: Design & Innovation | Design | GreenBiz.com, 2010-12-29 13:00:00 UTC
With the recent addition of recycled porcelain, ceramic tile maker Fireclay Tile has developed products with more than 70 percent recycled content.


New Yeast Strain Doubles the Efficiency of Biofuel Production
by: Inhabitat , 2010-12-28 22:35:07 UTC

A team of researchers has developed a new strain of yeast that could make the production of biofuels two times more efficient by breaking down an elusive sugar chain present in plant stems called xylose. Up until now, two processes have been used to break down all of the sugars contained in plants — one for simple sugars and one for complex sugars. This new yeast has the ability to break down simple and complex sugars at once, making the production of biofuels faster and yielding more end product.




Read the rest of New Yeast Strain Doubles the Efficiency of Biofuel Productionhttp://www.inhabitat.com/wp-admin/ohttp://www.inhabitat.com/wp-admin/options-general.php?page=better_feedptions-general.php?page=better_feed
Permalink |
Add to
del.icio.us |
digg
Post tags: biofuel, biofuel inefficiencies, biofuel production, efficient biofuel, how to make biofuel, inefficient biofuels, new biofuels, new yeast strain, yeast strain
Top 6 Green Technology Stories of 2010 – Vote for Your Favorite!
by: Inhabitat , 2010-12-29 01:43:04 UTC

Green technology has moved far beyond solar panels over the past decade, and the breakthroughs we’ve seen just over the last year have been nothing short of amazing. But the big ideas that made headlines this year weren’t just conceptual — in fact, many of the most impressive developments are or are well on their way to becoming life-changing realities! From consumer cell phones that harness your body heat for energy, to machinery that rethinks how we carry-out brick construction, to nano-particles that transform trees into public infrastructure, to LED-adorned contact lenses that could give way to bionic vision — check out our top 6 tech stories of the past year and don’t forget to vote for your #1 choice!
Note: There is a poll embedded within this post, please visit the site to participate in this post's poll.
Permalink |
Add to
del.icio.us |
digg
Post tags: 2010 technological innovations, 2010 technology, brick machine, brick roller, cell phones use body heat, green technology, led contact lenses, nano particles, Solar Power, sustainable technology, technology and the environment, top 6 green technology
New ‘plant mimicking’ machine generates fuels using solar energy
by: Ecofriend, 2010-12-28 09:10:46 UTC

Eco Factor: Machine generates hydrogen and syngas using solar energy.
A team of researchers in the US and Switzerland have created a machine that like plants uses solar energy to produce fuels, which can later be used in different ways. The machine makes use of the sun’s rays and a metal oxide called ceria to break down carbon dioxide or water in fuels that can be stored and transported. Unlike solar panels, which work only during the day, this new machine is designed to store energy for later use.
Ceria or cerium oxide has a natural property to exhale oxygen as it heats up and inhale as it cools down. In the prototype, carbon dioxide and water are pumped into the vessel ceria rapidly strips oxygen from them creating hydrogen and/or carbon monoxide. Hydrogen produced by the machine can be used in fuel cells, whereas hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be combined to produce syngas.

While the prototype does show a possible use of solar energy for producing energy through the night as well, the machine suffers from an efficiency problem. The prototype developed harnesses only 0.8 percent of incident solar energy to produce more energy, while a major portion is lost through the reactor’s wall or through the re-radiation of sunlight back through the device’s aperture. The research team is confident that the efficiency rates can be enhanced to 19 percent by making some improvements in insulation and by using smaller apertures.
Via: BBC



UW students develop low-cost solar-powered water purification system
by: Ecofriend, 2010-12-28 11:34:41 UTC

Eco Factor: Low-cost water disinfection system powered by solar energy.
The idea of using solar energy for purifying water has been around for ages and is still practiced in different parts of the globe. However, now a team of students from the University of Washington have come up with a bright idea taking a little bit of technical help to devise a low-cost solution to a global problem. Using simple parts, the student team has developed a cheap setup solution for drinking water in poor areas, which has won them a $40,000 prize.
The team reports that using parts from a keychain that blinks in response to light, they have created a device that monitors how light is passing through a water-filled bottle and how many particulates are obstructing the light. When enough particulates are removed, the sensor alerts that the water is now safe to drink. The student team believes that the device can be retailed at just $3.40, which makes it a viable solution for many parts of the world.
Via: Treehugger



Top 10 renewable energy technology breakthroughs in 2010
by: Ecofriend, 2010-12-29 12:29:01 UTC

With our planet in a desperate need of new eco-friendly energy generating systems, researchers over the globe have been working hard to develop systems that can power the world of the future in a sustainable fashion. The year 2010 saw some great breakthroughs in the field of renewable energy technology, which when fully developed, could help create a better world. Here we have compiled a list of 10 such breakthroughs that are bound to have a significant impact in the future.
• IBM’s solar cell created from “earth abundant” materials

Researchers at IBM created an inexpensive solar cell from materials that are dirt cheap and easily available. The layer that absorbs sunlight and converts it into electricity is made with copper, tin, zinc, sulfur and selenium. The best part of the solar cell is that it still manages to hit an efficiency of 9.6 percent, which is much higher than earlier attempts to make solar panels using similar materials.
• MIT’s Concentrated Solar Funnel

A group of researchers at MIT devised a way to collect solar energy 100 times more concentrated than a traditional photovoltaic cell. The system could drastically alter how solar energy is collected in the near future as there will no longer be a need to build massive solar arrays to generate large amounts of power. The research work conducted has determined that carbon nanotubes will be the primary instrument used in capturing and focusing light energy, allowing for not just smaller, but more powerful solar arrays.
• Wake Forest University’s Light Pipes

Researchers at the Wake Forest University in North Carolina made a breakthrough by developing organic solar cells with a layer of optical fiber bristles that doubles the performance of the cells in tests. The prototype solar cell has been developed by David Carroll, who is the chief scientist at a spin-off company called FiberCell. The problem with standard flat panels is that some sunlight is lost through reflection. To reduce this effect, the research team took a dramatic approach by stamping optical fibers onto a polymer substrate that forms the foundation of the cell. These fibers, dubbed the “Light Pipes,” are surrounded by thin organic solar cells applied using a dip-coating process, and a light absorbing dye or polymer is also sprayed onto the surface. Light can enter the tip of a fiber at any angle. Photons then bounce around inside the fiber until they are absorbed by the surrounding organic cell.
• Louisiana Tech University’s CNF-PZT Cantilever

Created by a research team at Louisiana Tech University, the CNF-PZT Cantilever is a breakthrough energy harvesting device, which utilizes waste heat energy from electronic gadgets to power them. The device features the use of a carbon nanotube on a cantilever base of piezoelectric materials. The carbon nanotube film absorbs heat and forces the piezoelectric cantilever to bend, which then generates an electric current in the material. The device is so small that thousands of small CNF-PZT Cantilever devices can be designed into devices, allowing them to harvest their own wasted energy.
• New Energy Technologies’ see-through glass SolarWindow

New Energy Technologies developed a working prototype of the world’s first glass window capable of generating electricity. Until now, solar panels have remained opaque, with the prospect of creating a see-through glass window capable of generating electricity limited by the use of metals and other expensive processes, which block visibility and prevent light from passing through glass surfaces. The technology has been made possible by making use of the world’s smallest working organic solar cells, developed by Dr. Xiaomei Jiang at the University of South Florida. Unlike conventional solar systems, New Energy’s solar cells generate electricity from both natural and artificial light sources, outperforming today’s commercial solar and thin-film technologies by as much as 10-fold.
• Purdue University’s system to harvest heat from car’s exhaust

Researchers at Purdue University created a system that harvests heat from a car’s exhaust in order to generate electricity and reduce the vehicle’s fuel consumption. The system converts waste heat into electricity, which is then fed into the vehicle’s onboard batteries to reduce engine load and fuel consumption.
• Innowattech’s Piezoelectric IPEG PAD

Innowattech recently created piezoelectric generators that can be used as normal rail pads, but generate renewable energy whenever trains pass on them. The company tested the technology by replacing 32 railway pads with new IPEG PADs, where the pads were able to generate enough renewable electricity to determine the number of wheels, weight of each wheel and the wheel’s position. In addition the speed of the train and wheel diameter could also be calculated. The company states that areas of railway track that get between 10 and 20 ten-car trains an hour can be used to produce up to 120KWh of renewable electricity per hour, which can be used by the railways or transferred to the grid.
• Sony’s Flower Power

Sony recently demonstrated new DSSC’s for energy generating windows, which help beautify your home as well. The beautifully designed solar panels make use of screen printing to generate custom designs according to the consumer’s preferences. The panels can be developed in any color that the user specifies.
• Plant mimicking machine produces fuels using solar energy

A team of researchers in the US and Switzerland have created a machine that like plants uses solar energy to produce fuels, which can later be used in different ways. The machine makes use of the sun’s rays and a metal oxide called ceria to break down carbon dioxide or water in fuels that can be stored and transported. Unlike solar panels, which work only during the day, this new machine is designed to store energy for later use.
• CSIRO’s Brayton Cycle Project

Australia’s national science agency, CSIRO, developed a technology that requires only sunlight and air to generate electricity. The system is ideal for areas that face acute water shortages. The solar Brayton Cycle project replaces use of concentrated sun rays to heat water into high-pressure steam to drive a turbine with solar energy to create a solar thermal field. The technology focuses the sun’s rays projected onto a field of mirrors knows as heliostats onto a 30-meter (98 ft) high solar tower to heat compressed air, which subsequently expands to through a 200kW turbine to generate electricity.












Comments by our Users
Be the first to write a comment for this item.